WHAT IS VITAMIN K1?
Phylloquinone, often known as vitamin K1, is a fat-soluble vitamin necessary for healthy blood coagulation and bones. In order to ensure that wounds may heal properly and that excessive bleeding is avoided, it plays a key function in the activation of proteins involved in the coagulation process. Green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli as well as some oils like soybean and canola oil are the main sources of vitamin K1. It is utilised for blood coagulation and other essential bodily processes after being absorbed in the small intestine and stored in the liver.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/foods-high-in-vitamin-k-5114127-no-text-FINAL-4a2cb81a6d314dbeba059758354704af.png)
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF VITAMIN K1?
Scientifically known as phylloquinone, vitamin K1 is an essential component with a number of health advantages. Here are some key benefits of supplementing vitamin K1
- Blood Clotting Regulation: One of vitamin K1’s main roles is to regulate blood clotting. Your body needs to create a clot in order to halt bleeding after a cut or other injury. Because it activates several clotting proteins in the liver that aid in the formation of a stable blood clot, vitamin K1 is crucial for this process. Blood coagulation would be compromised without enough vitamin K1, increasing the risk of excessive bleeding. However, a delicate balance must be maintained since too much vitamin K1 might encourage excessive blood clotting, which may exacerbate cardiovascular problems. Therefore, maintaining adequate blood coagulation and preventing haemorrhage require a sufficient yet moderate consumption of vitamin K1.
- Bone Health: Vitamin K1 is important for bone health in addition to its involvement in blood clotting. It is involved in the protein osteocalcin’s activation, which controls how calcium is incorporated into bone tissue. For appropriate bone mineralization and strength, a process called as carboxylation is required. An essential mineral for maintaining strong and healthy bones, especially as we age, vitamin K1 is linked to increased bone density and a decreased risk of fractures.
- Cardiovascular health: A growing body of research indicates that vitamin K1 may help to maintain cardiovascular health. According to some research, people who consume more vitamin K1 may be at a lower risk of developing coronary artery disease. Vitamin K1’s role in controlling calcium, which is essential for blood clotting as well as avoiding the hardening of the arteries, may be the cause of this potential benefit. Vitamin K1 may support healthier blood vessels and a lower risk of heart-related problems by aiding in calcium homeostasis.
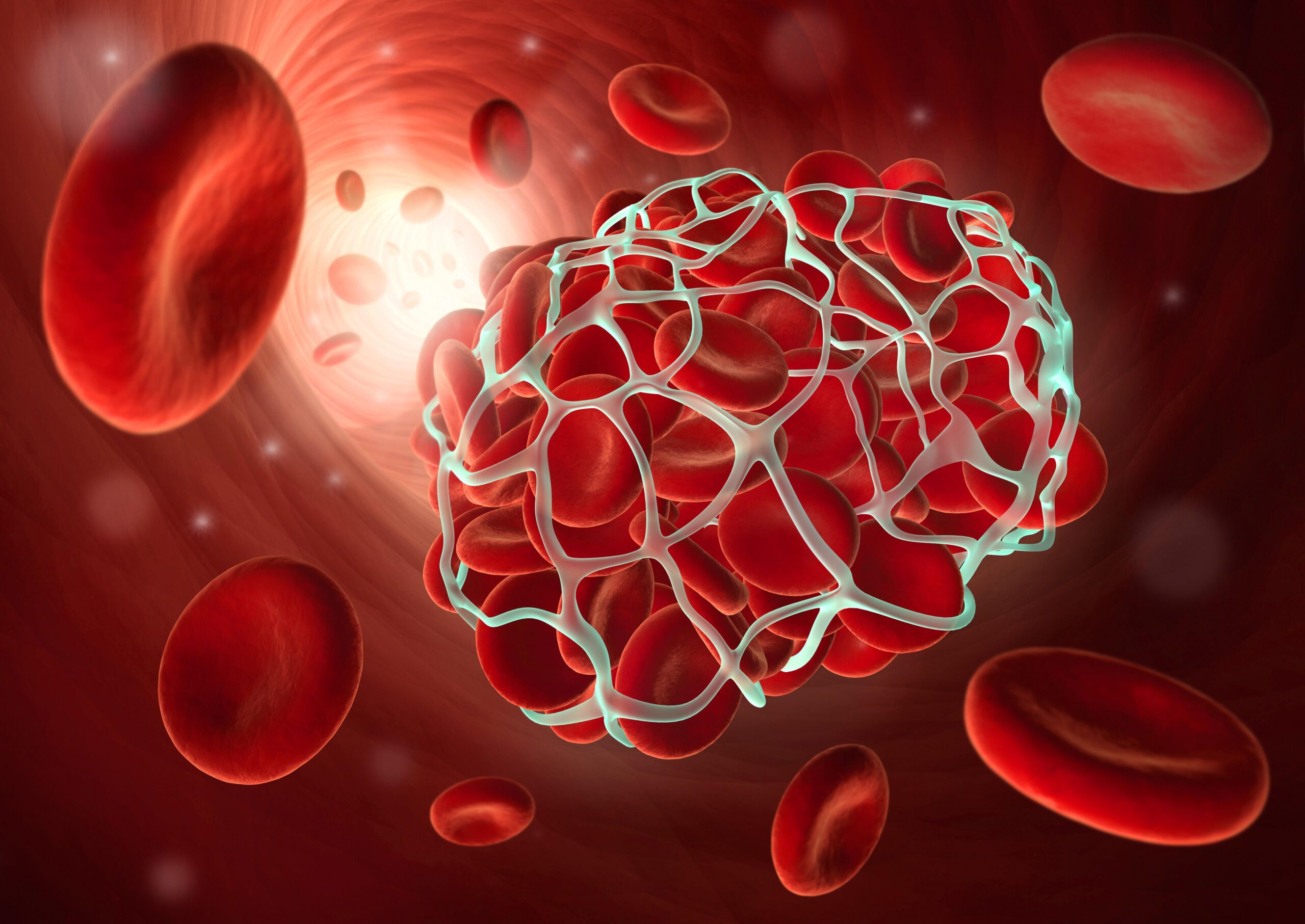
In conclusion, vitamin K1 is important for many areas of our health while frequently being overlooked in favour of other vitamins. Vitamin K1 is deserving of praise for its many advantages, which include maintaining efficient blood clotting, boosting bone strength, and maybe improving cardiovascular health.
HOW DOES VITAMIN K1 WORK IN HUMAN BODY?
Following consumption, vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, is essential for a number of vital bodily functions. After consumption, it is predominantly absorbed in the small intestine. After being ingested, it travels via the bloodstream and is carried to the liver for storage. Vitamin K1 is used in the liver to create clotting factors, a group of different proteins involved in blood clotting. Prothrombin, as well as factors VII, IX, and X, are among these clotting factors.
The body starts a complicated chain of events known as the coagulation cascade in response to an injury or wound that destroys blood vessels in order to create a blood clot and halt bleeding. Because it gives these clotting factors a chemical “tag” or carboxyl group, a process known as carboxylation, vitamin K1 is crucial for this procedure. These proteins can now bind to calcium ions, which is essential for their role in the formation of a stable blood clot. Lack of vitamin K1 increases the risk of uncontrolled bleeding because it impairs the generation of effective clotting components.
Vitamin K1, in addition to aiding in blood clotting, also promotes the health of bones by assisting in the activation of osteocalcin, a protein that controls the absorption of calcium into bone tissue. This process helps to maintain the mineralization of bones and overall skeletal strength.
HOW MUCH VITAMIN K1 CAN A PERSON TAKE?
Phylloquinone, often known as vitamin K1, has different suggested intakes based on a variety of variables, including age, gender, and particular medical conditions. The recommended daily intake (RDI) for vitamin K for adults is normally 50 micrograms (mcg) per day, which is the lowest effective amount. This quantity is thought to be adequate for maintaining healthy bones and regular blood coagulation in the general population. A balanced diet that includes items like green leafy vegetables (such as spinach, kale, and broccoli) and specific oils (such as soybean and canola oil) is often the best way to ensure that one is getting an adequate amount of vitamin K1.
The maximum daily dose for vitamin K1, on the other hand, is substantially greater, at 10,000 micrograms (10 milligrammes, or 10 mg). When consumed orally, this higher level, which is far above the RDI, is typically regarded as safe for the majority of people. It’s crucial to remember that such large doses are often employed in therapeutic contexts, for example, in the treatment of particular medical disorders, like vitamin K insufficiency, or to neutralise the effects of specific blood-thinning drugs. Before taking vitamin K1 supplements at levels much over the RDI, people should speak with a healthcare provider because extremely high intakes may interact with drugs or worsen underlying health issues.
These dosage guidelines are supported by research, which shows that an average adult only requires about 50 mcg of vitamin K per day, but greater dosages of up to 10,000 mcg can be supplied safely in certain medical situations. As with any dietary supplement, it’s critical to seek advice from a healthcare professional to establish the right dosage based on your health needs and to prevent any potential interactions or negative effects.
WHAT ARE THE VARIATIONS OF VITAMIN K1?
Vitamin K1 is also available as:
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone / Phytomenadione / Phytonadione) 0.1% Powder
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone / Phytomenadione / Phytonadione) 0.25% Powder
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone / Phytomenadione / Phytonadione) 1% Food State On Yeast
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone / Phytomenadione / Phytonadione) 1% Powder
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone / Phytomenadione / Phytonadione) 20% Powder
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone / Phytomenadione / Phytonadione) 5% (in Olive Oil)
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone / Phytomenadione / Phytonadione) 5% Powder
Vitamin K1 is commonly available in:
- Vitamin K1 tablets
- Vitamin K1 capsules
- Vitamin K1 powder
Glentworth Formulations is here to suit your every need. Everything from Tablets, Capsules and Powder blends.
If you are wanting to know more information, please get in contact with us. Either using the contact form or contacting us directly on: [email protected].


