WHAT IS MANGANESE?
Manganese is an essential trace mineral that supports several body activities. Although your body may retain a tiny amount of manganese in vital organs like the bones, kidneys, liver, and pancreas, it is crucial to get an adequate quantity through your food. The proper operation of your brain, neurological system, and other enzyme systems depends on this trace mineral. Rich supplies of manganese can be found in seeds and whole grains, while legumes, beans, nuts, leafy green vegetables, and tea also contain minor levels of the mineral. Its status as an essential nutrient emphasises how crucial it is to include foods high in manganese in your diet to maintain good health and wellbeing.
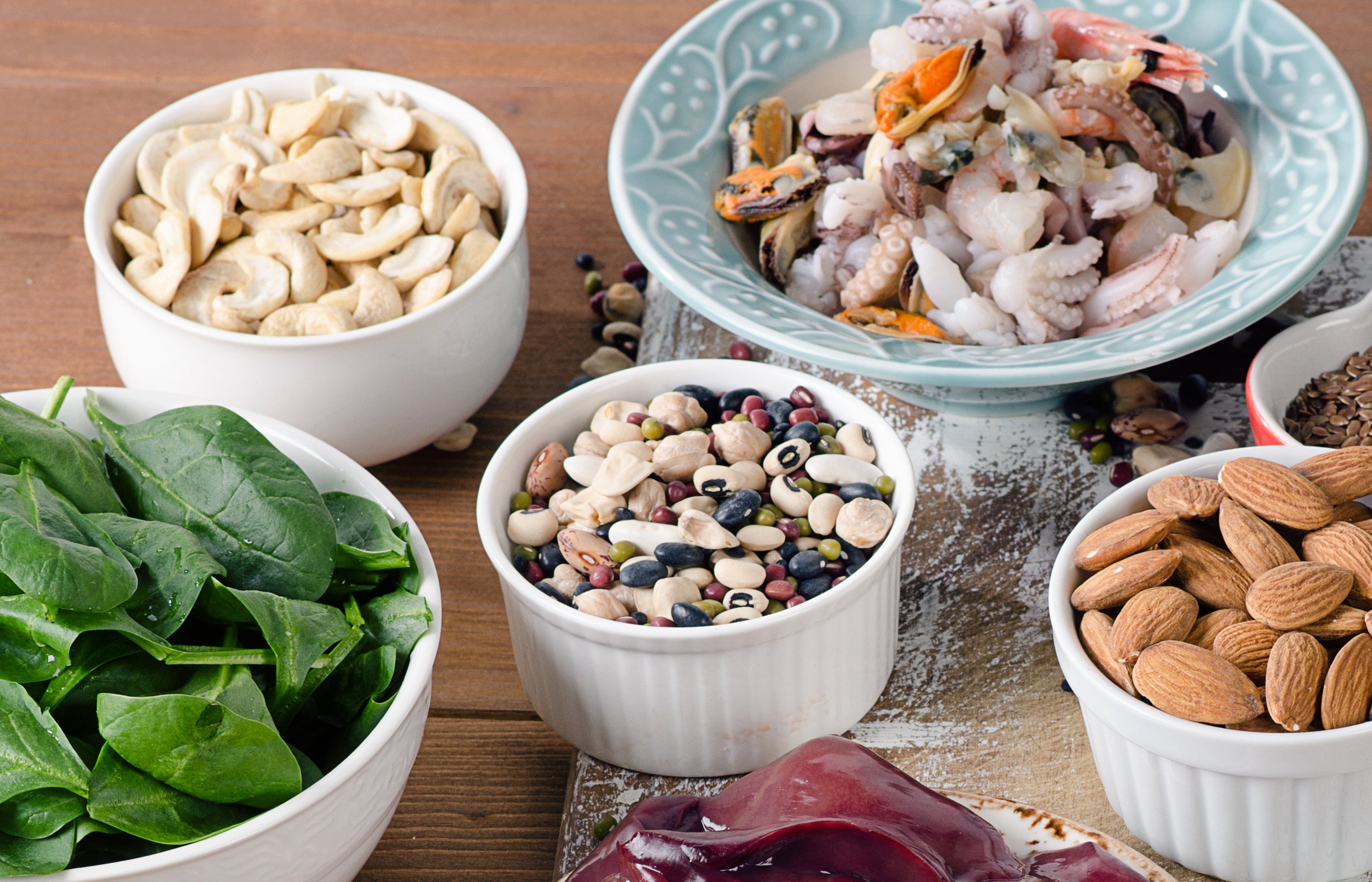

WHAT ARE THE HEALTH BENEFITS OF MANGANESE?
When manganese, a key trace mineral, is included in your diet, it provides a number of health benefits. Its role in enhancing bone health is one of its significant benefits, especially when paired with other crucial minerals like calcium, zinc, and copper. Here are some of its amazing benefits:
- May Improve Bone Health: Manganese is essential for bone health because it acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in bone growth and maintenance. One of its most important jobs is to work with key minerals like calcium, zinc, and copper to increase bone mineral density. This coordinated effort is particularly important for older persons who are at risk of osteoporosis-related fractures. Osteoporosis, characterised by brittle and frail bones, is a major concern to the elderly, particularly postmenopausal women. According to research, 50% of postmenopausal women and 25% of males aged 50 and up will suffer from osteoporosis-related fractures. To mitigate this danger, research have investigated the potential of manganese in combination with other important bone-supporting minerals.
- Rich in Antioxidants: Manganese plays an important role in the antioxidant defence system of the body, primarily through its role in the synthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD). SOD is an important antioxidant enzyme that plays an important role in neutralising free radicals, which are highly reactive chemicals that cause cellular damage. The ability to combat the harmful effects of free radicals is critical, as these molecules have been linked to a variety of age-related disorders, including heart disease and some malignancies. Superoxide dismutase acts as a cellular protector by converting superoxide, a particularly dangerous free radical, into smaller, harmless molecules that do not harm your cells.
- Reduce Inflammation: Manganese’s contributions to health extend to inflammation, with potential advantages for people suffering from chronic inflammation-related illnesses including osteoarthritis. While inflammation is an important aspect of the immune response, persistent inflammation can cause a variety of health problems, including joint pain and damage. Manganese‘s interaction with superoxide dismutase (SOD), a powerful antioxidant enzyme, is one of the routes through which it may produce anti-inflammatory effects. Several investigations have revealed that manganese-influenced SOD can be helpful in inflammatory diseases. This has been studied specifically in relation to osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint condition marked by severe inflammation and cartilage loss.
However, these benefits, especially when paired with other important minerals, highlight the necessity of adding manganese-rich foods in your diet to enhance general well-being and potentially lower the risk of certain diseases. As with any nutritional concern, consulting with a healthcare expert is recommended to ensure individualised and evidence-based recommendations.
HOW MUCH MANGANESE SHOULD YOU TAKE A DAY?
Manganese has an Adequate Intake (AI) recommendation of 1.8 to 2.3 milligrammes (mg) per day, however there is no precise Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) specified for this trace mineral. Manganese consumption may vary depending on factors such as age and specific health concerns. The AI of children fluctuates with age.
It’s critical to use caution when taking manganese supplements, as too much can be harmful to your health. Manganese’s Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) in individuals 19 and older is established at 11 mg per day. Manganese, like other heavy metals such as zinc, copper, selenium, and iron, should be ingested in moderation to avoid potential toxicity.
Manganese is required for a variety of body activities, and deficits can be treated therapeutically either oral supplementation or, in more severe situations, intravenous (IV) treatment for people who have been recognised as deficient. While supplementation is an option, many foods contain manganese naturally, making it available through a well-balanced diet. Manganese-rich foods include seeds, whole grains, legumes, beans, nuts, leafy green vegetables, and tea. To maintain optimal health and avoid potential toxicity, it is best to get manganese through diet and get advice from a healthcare practitioner or nutritionist when considering supplementation.
WHAT MANGANESE DOES FOR THE BODY?
When manganese, an essential trace mineral, is consumed, it plays an important function in a variety of physiological processes. It functions as a cofactor for various enzymes engaged in critical metabolic activities. It serves as a cofactor for enzymes involved in antioxidant defence systems, which is one of its key activities. Manganese helps to build and activate superoxide dismutase (SOD), an important antioxidant enzyme that protects cells from oxidative damage. SOD reduces the risk of cellular damage and potential health issues associated with oxidative damage, such as ageing and chronic diseases, by converting destructive superoxide radicals into less dangerous chemicals.
Manganese also has a role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, amino acids, and cholesterol. It aids the body’s utilisation of certain macronutrients by acting as a cofactor for enzymes involved in the breakdown and utilisation of these substances. Furthermore, manganese aids in the manufacture of glycosaminoglycans, which are key components of connective tissues and are required for the maintenance of healthy joints and cartilage. Overall, manganese’s role in enzymatic activities and contribution to antioxidant defences make it an important mineral for sustaining optimal health and well-being when ingested in sufficient proportions.
WHAT ARE THE VARIATIONS OF MANGANESE SUPPLEMENTS?
Note that MANGANESE is also available as:
- Manganese 1.5% Food State On Buckwheat (~1.5% Mn)
- Manganese 5% Food State On Yeast (~5% Mn)
- Manganese Aspartate Nutrition Grade (~14% Mn)
- Manganese Bisglycinate Nutrition Grade (~16% Mn)
- Manganese Gluconate Nutrition Grade (~11% Mn)
- Manganese Picolinate Nutrition Grade (~18% Mn)
- Manganese Sulphate Monohydrate Nutrition Grade (~36% Mn)
MANGANESE is commonly available in:
- Manganese tablets
- Manganese capsules
- Manganese powders
Glentworth Formulations is here to suit your every need. Everything from Tablets, Capsules and Powder blends.
If you are wanting to know more information, please get in contact with us. Either using the contact form or contacting us directly on: [email protected].


